Introduction
 Photo by Blake Wisz on Unsplash
Photo by Blake Wisz on Unsplash
This material was originally part of a university course I created on data science and machine learning. I've reorganized the pages a bit and indexed them here to make them easier for the general public to make use of the information.
If you're a student in CSE 450, this probably isn't the page you're looking for. I would suggest the official course index found here.
Some of the readings make reference to the course textbook Fundamentals of Machine Learning for Predictive Data Analytics (1st edition), which I highly recommend.
Though you can almost certainly find alternative sources for the topics covered in the text by googling, the book does a great job of providing a high level overview of the topic, as well as covering the math and statistics needed to adequately understand how a particular topic should be used (and when it shouldn't be).
The course is designed around a series of two-week modules, though the exact timing doesn't matter so much outside of a traditional classroom setting.
Resources and Tips
Here are some tips and reference pages we provided to students to help them succeed in the course:
Module One: A Crash Course in Data Analytics and Visualization
The first module has four topics. Each assignment is designed to introduce one or more topics of data analytics and visualization, and to give students practice taking a business problem and re-framing it as an analytics or visualization problem.
Each topic has a Preparation reading that covers the theory, math, and statistical background of a given topic, as well as some references and tips for the coding aspects of the topic. This is followed by a Data Exploration assignment presented in the form of a simulated case-study.
Classroom Implementation Tips
The first module is designed as a refresher/fast introduction into data wrangling and visualization using Python. Most of the students taking this course had had exposure to one or more of these topics in previous courses, but that wasn't always the case.
At the end of the first module, a self-evaluation assignment allows students to determine how likely they are to be able to move forward with the course successfully.
The timing of this assessment falls prior to the drop/add deadline, which gave me a chance to sit down with students and recommend alternative preparatory courses as needed.
1. Netflix Movies
 Photo by Mollie Sivaram on Unsplash
Photo by Mollie Sivaram on Unsplash
Topics Covered
- Learn to understand the difference between types of machine learning problems (supervised vs. unsupervised, classification vs. regression, etc...).
- Learn the "parts" and vocabulary of machine learning problems.
- Learn how to use Google Colab.
- Learn how to load, explore, and filter data with the Pandas library.
- Look at different options for data visualization.
2. Cereal Marketing
 Photo by Haley Owens on Unsplash
Photo by Haley Owens on Unsplash
Topics Covered
- Review of basic statistics
- Data exploration and visualization.
- Calculating summary statistics.
- Feature engineering.
3. Titanic Survival Patterns
 Photo by Derek Oyen on Unsplash
Photo by Derek Oyen on Unsplash
Topics Covered
- Analyzing feature relationships using statistics and visualizations.
- Feature engineering
- Feature encoding
4. Flower Classification
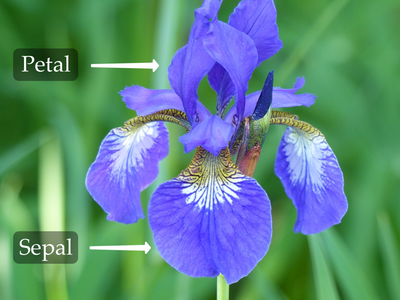
Topics Covered
- The k-Nearest Neighbors algorithm.
- How to evaluate model performance.
- Become familiar with the Scikit Learn machine learning library
- Use the library to build a machine learning model.
- Use that model to make predictions.
Self-Assessment
This assignment is designed to assess how well students understood the topics from the previous five assignments by testing their ability to apply the concepts to similar, but different situations.
Modules Two - Six: An Applied Survey of Machine Learning Topics
In each of the remaining modules, students learn about the theory and application of a machine learning algorithm through a preparation reading assignment.
Each reading also introduces auxiliary topics, such as feature engineering, model evaluation techniques, and tuning of hyperparameters.
For each topic, a business problem is then introduced through a Case Study Intro, where students learn about the business problem, and the primary concerns of the key stakeholders.
The students then engage in an In-class Case Study Discussion where stakeholders ask questions of the "data science team". Students discuss the question as a team and then share their answers and the reasoning behind them. Some questions have a particularly correct answer, while others have multiple answers that each have a reasonable amount of merit.
Students then start the Case Study Project, which outlines key deliverables the stakeholders are interested in.
Classroom Implementation Tips
If you're adopting this course for use in a classroom, here are some implementation notes that will make this more successful:
-
The course was designed for teams of around 3-6 people to work together, with a rotating "project manager role".
-
A strong emphasis is placed on reporting back to the stakeholders by translating machine learning results back into the context of actionable business insights.
-
Module grades are comprised almost entirely from the self-evaluation and peer-evaluations that form part of the module postmortem.
-
Be sure to have students read the Team Project Expectations Guide to help them achieve this.
-
I always invited students to take turn role-playing stakeholders for the in-class discussion assignments. There are some recurring characters, and many students really enjoyed this aspect of making it feel more realistic.
-
Also related to adding to the realism, whenever students had a question about a case study, I required them to send a message to the stakeholder they thought would best be able to answer the question (via email or Slack). I then answered the question from the point of view of the stakeholder.
Module 02: Banking and Market Segmentation
 Photo by Ricardo Resende on Unsplash
Photo by Ricardo Resende on Unsplash
This module covers decision trees, and more model evaluation methods (ROC and AUC) within the context of a Portuguese bank that wants to engage in some targeted marketing efforts.
Module 03: House Price Estimation
 Photo by Campaign Creators on Unsplash
Photo by Campaign Creators on Unsplash
This module covers model ensembles, gradient boosted trees, and using the XGBoost library to solve regression tasks within the context of a real estate firm that wants to use machine learning to improve the accuracy of their housing valuations.
Module 04: Bike Rentals and Resource Planning
 Photo by Markus Winkler on Unsplash
Photo by Markus Winkler on Unsplash
This module introduces basic neural networks within the context of a bike rental startup that wants to find a better way to handle staff and inventory planning.
Module 05: Self Driving Cars and Computer Vision
 Photo by Campbell Boulanger on Unsplash
Photo by Campbell Boulanger on Unsplash
This module introduces convolutional neural networks and data augmentation within the context of an automotive company doing research into self-driving cars.
Module 06: AI Content Generation
 Photo by Bank Phrom on Unsplash
Photo by Bank Phrom on Unsplash
This module introduces recurrent neural networks within the context of a publishing company seeking to expand its catalogue using AI-generated content.
"Bonus" modules
These modules were cut from the course either due to fit in more relevant algorithms, or due to other issues with the data.
KNN Module: Predicting Hits from Spotify Data
 Photo by Austin Neill on Unsplash
Photo by Austin Neill on Unsplash
Before we had kNN as part of the flower classification assignment in week 01, we had an entire module on the topic, framed within the context of a record label trying to identify trends in top songs based on metrics in Spotify data.
The module covered kNN in a bit more detail than the module one assignment does, but after a couple of iterations of the course, we found this problem to be a bit ill-defined, and students were having trouble producing actionable insights from the data, so I ultimately cut the module and distilled the key points into module one.
Clustering Module: DE&I in the Workplace
 Photo by Campaign Creators on Unsplash
Photo by Campaign Creators on Unsplash
I loved the premise of this topic - evaluating hiring practices and salary trends to be able to quantitatively answer questions about workplace diversity and pay gap issues. It also was the only module in the course that covered unsupervised learning (via k-Means Clustering).
Unfortunately, the dataset had a lot of underlying issues due to how it was generated, which led to students coming to some pretty obvious conclusions too quickly.
At the same time, we really wanted to make room for RNNs, which we felt was more important for our students to understand than unsupervised learning. So this module was ultimately cut from the course.